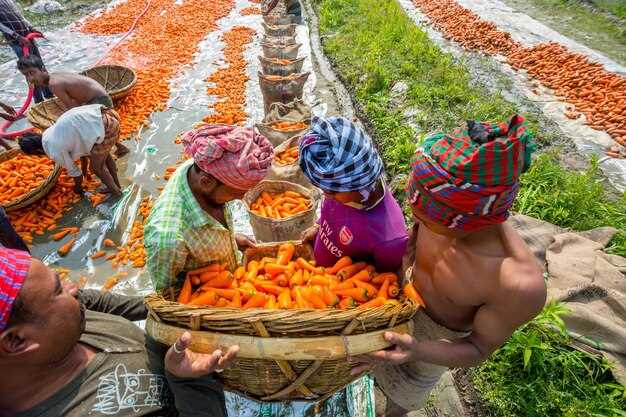
In the quest for a resilient and self-sufficient agricultural system, the Kingdom of Cambodia has embarked on a transformative journey towards sustainable farming practices. By embracing innovative approaches and fostering a harmonious relationship between humans and nature, Cambodia aims to secure a steady supply of nutritious food for its population. This article delves into the multifaceted strategies employed by the nation to bolster its agricultural sector, ensuring long-term food sufficiency and promoting environmental stewardship.
Empowering Farmers through Knowledge and Technology
At the heart of Cambodia’s sustainable farming revolution lies the empowerment of its farmers. Recognizing their pivotal role in the nation’s food security, efforts have been made to equip them with the necessary knowledge and tools to adopt sustainable practices. Through comprehensive training programs and workshops, farmers are educated on the benefits of organic farming, crop rotation, and integrated pest management. By embracing these techniques, farmers can minimize the use of harmful chemicals, preserve soil fertility, and safeguard the health of both consumers and the environment.
Furthermore, Cambodia has embraced the potential of technology to revolutionize its agricultural landscape. By harnessing the power of digital platforms and mobile applications, farmers can access real-time information on weather patterns, market prices, and best farming practices. This enables them to make informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and enhance overall productivity. The integration of technology not only empowers farmers but also fosters a sense of connectivity and collaboration within the agricultural community.
Diversification and Resilience: The Key to Food Security
In the face of climate change and other external challenges, Cambodia recognizes the importance of diversifying its agricultural sector to ensure food security. By promoting the cultivation of a wide range of crops, the nation reduces its reliance on a single crop and mitigates the risks associated with crop failure. Emphasis is placed on the cultivation of climate-resilient crops that can withstand adverse weather conditions and thrive in diverse ecosystems.
Moreover, Cambodia encourages the adoption of agroforestry practices, integrating trees and shrubs into agricultural landscapes. This not only enhances biodiversity but also provides additional sources of income through the cultivation of fruits, nuts, and timber. Agroforestry systems contribute to soil conservation, water retention, and carbon sequestration, making them an integral part of Cambodia’s sustainable farming strategy.
Preserving Cultural Heritage and Local Wisdom
As Cambodia strives towards sustainable agriculture, it recognizes the importance of preserving its rich cultural heritage and traditional farming practices. Local wisdom, passed down through generations, holds invaluable insights into sustainable farming techniques that are adapted to the local climate and ecosystem. By integrating traditional knowledge with modern innovations, Cambodia ensures the preservation of its cultural identity while embracing the advancements of the future.
Furthermore, Cambodia promotes the consumption of indigenous crops and traditional food systems, which not only contribute to food security but also safeguard the nation’s unique biodiversity. By valuing and preserving its cultural heritage, Cambodia paves the way for a sustainable future that is deeply rooted in its past.
The Importance of Sustainable Agriculture for Food Security
In the context of promoting a secure and reliable food supply, the significance of sustainable agricultural practices cannot be overstated. By adopting methods that prioritize long-term environmental, social, and economic viability, sustainable agriculture plays a pivotal role in ensuring food security for present and future generations. This section explores the various reasons why sustainable agriculture is crucial for maintaining a stable and accessible food system.
Preserving Natural Resources
Sustainable agriculture recognizes the finite nature of natural resources and aims to minimize their depletion. By implementing practices such as crop rotation, organic fertilization, and water conservation, farmers can maintain soil fertility, prevent erosion, and preserve water quality. These measures not only safeguard the environment but also contribute to the long-term productivity and resilience of agricultural systems, ensuring a consistent supply of nutritious food.
Enhancing Resilience to Climate Change
As the impacts of climate change become increasingly evident, sustainable agriculture offers a pathway to adapt and mitigate its effects. By diversifying crops, implementing agroforestry techniques, and adopting climate-smart practices, farmers can build resilience against extreme weather events, pests, and diseases. This adaptability not only safeguards food production but also reduces vulnerability to climate-related disruptions, ensuring food security in the face of a changing climate.
Furthermore, sustainable agriculture practices contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, thus mitigating climate change. By minimizing the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, adopting precision agriculture techniques, and promoting agroecological approaches, farmers can play a vital role in combating climate change and its adverse effects on food security.
In conclusion, the importance of sustainable agriculture for food security cannot be overstated. By preserving natural resources, enhancing resilience to climate change, and mitigating environmental impacts, sustainable agricultural practices ensure a reliable and accessible food supply for current and future generations. Embracing sustainable agriculture is not only essential for the well-being of individuals and communities but also for the long-term sustainability of our planet.
Challenges Faced by Cambodia in Achieving Food Security
Addressing the complex issue of ensuring food security in Cambodia presents numerous challenges that need to be overcome. These obstacles hinder the country’s ability to achieve a sustainable and reliable food supply for its population. This section will explore some of the key challenges faced by Cambodia in its pursuit of food security.
1. Limited Agricultural Resources
Cambodia faces the challenge of limited agricultural resources, including arable land, water availability, and suitable climate conditions for crop cultivation. The country’s agricultural sector is predominantly rain-fed, making it vulnerable to climate change impacts such as droughts and floods. Additionally, the rapid urbanization and industrialization have led to the conversion of agricultural land for other purposes, further reducing the available resources for food production.
2. Lack of Access to Modern Farming Techniques
The majority of farmers in Cambodia still rely on traditional farming methods, which often result in low productivity and inefficient resource utilization. Limited access to modern farming techniques, such as improved seeds, fertilizers, and mechanization, hinders the country’s ability to increase agricultural productivity and meet the growing demand for food. The lack of knowledge and training on sustainable farming practices also contributes to this challenge.
| Challenges | Impact |
|---|---|
| Limited agricultural resources | Reduced food production capacity |
| Lack of access to modern farming techniques | Low agricultural productivity |
These challenges, among others, pose significant obstacles to Cambodia’s efforts in achieving food security. Addressing these issues requires a comprehensive approach that includes sustainable agricultural practices, investment in agricultural infrastructure, and capacity building for farmers. By overcoming these challenges, Cambodia can enhance its food security and ensure a sustainable future for its population.
Government Initiatives to Promote Sustainable Agriculture

The government of Cambodia has implemented various strategies and programs to foster the development of environmentally-friendly and economically-viable agricultural practices. These initiatives aim to ensure the long-term viability of the agricultural sector, enhance food production, and improve the livelihoods of farmers.
One of the key government initiatives is the promotion of organic farming methods. By encouraging farmers to adopt organic practices, such as the use of natural fertilizers and pest control methods, the government aims to reduce the reliance on chemical inputs and minimize the negative impact on the environment. This initiative also seeks to enhance the quality and safety of agricultural products, meeting the increasing demand for organic produce both domestically and internationally.
In addition to organic farming, the government has also prioritized the development of sustainable irrigation systems. By investing in the construction and maintenance of irrigation infrastructure, the government aims to improve water management in agriculture, ensuring efficient water use and reducing the risk of water scarcity. These initiatives not only support crop productivity but also contribute to the overall resilience of the agricultural sector in the face of climate change.
Furthermore, the government has established farmer training and extension programs to provide technical knowledge and skills to farmers. These programs aim to enhance farmers’ understanding of sustainable agricultural practices, including crop rotation, agroforestry, and integrated pest management. By equipping farmers with the necessary skills and knowledge, the government aims to empower them to adopt sustainable practices and improve their agricultural productivity.
Moreover, the government has implemented policies to promote the diversification of agricultural production. By encouraging farmers to cultivate a variety of crops, including both staple and high-value crops, the government aims to enhance food security, increase farmers’ income, and reduce the vulnerability of the agricultural sector to market fluctuations. These policies also promote sustainable land use practices, such as crop rotation and intercropping, which help maintain soil fertility and reduce the risk of pests and diseases.
In conclusion, the government of Cambodia has taken significant steps to promote sustainable agriculture through various initiatives. By focusing on organic farming, sustainable irrigation systems, farmer training, and diversification of agricultural production, the government aims to ensure the long-term viability of the agricultural sector, enhance food production, and improve the livelihoods of farmers.
Role of NGOs in Supporting Sustainable Agriculture
NGOs play a crucial role in promoting and advancing sustainable agricultural practices, thereby contributing to the overall development and food security of Cambodia. These organizations work tirelessly to address the challenges faced by farmers and rural communities, fostering innovation, knowledge sharing, and capacity building.
Advocacy and Policy Influence
NGOs actively engage in advocacy efforts to shape agricultural policies and practices that prioritize sustainability and resilience. They collaborate with government agencies, research institutions, and other stakeholders to influence decision-making processes and ensure that sustainable agriculture remains a key priority on the national agenda. By advocating for supportive policies, NGOs create an enabling environment for farmers to adopt sustainable practices and improve their livelihoods.
Capacity Building and Knowledge Sharing
NGOs play a vital role in building the capacity of farmers and rural communities by providing training, workshops, and technical assistance. They equip farmers with the necessary skills and knowledge to implement sustainable agricultural practices, such as organic farming, agroforestry, and water management techniques. Through knowledge sharing platforms, NGOs facilitate the exchange of best practices, innovative ideas, and scientific research, empowering farmers to make informed decisions and adapt to changing environmental conditions.
| NGO Initiatives | Description |
|---|---|
| Farmers’ Field Schools | NGOs establish Farmers’ Field Schools where farmers learn practical skills and techniques through hands-on training and demonstrations. |
| Market Linkages | NGOs facilitate market linkages for small-scale farmers, connecting them with buyers and ensuring fair prices for their produce. |
| Community-Based Seed Banks | NGOs establish community-based seed banks to preserve traditional crop varieties and promote biodiversity. |
Furthermore, NGOs collaborate with local communities to develop and implement sustainable agricultural projects, such as community gardens, sustainable irrigation systems, and climate-smart farming techniques. These initiatives not only enhance food security but also promote environmental conservation and resilience in the face of climate change.
In conclusion, NGOs play a pivotal role in supporting sustainable agriculture in Cambodia. Through advocacy, capacity building, and knowledge sharing, these organizations empower farmers and rural communities to adopt sustainable practices, improve their livelihoods, and contribute to the overall food security and development of the country.
Innovative Technologies for Sustainable Agriculture in Cambodia
In this section, we will explore the cutting-edge technologies that are revolutionizing the agricultural landscape in Cambodia. These innovative solutions are aimed at promoting sustainable practices and ensuring food security in the country.
One of the key advancements in sustainable agriculture is the use of precision farming techniques. This approach involves the application of technology, such as GPS and remote sensing, to optimize the use of resources such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides. By precisely targeting these inputs, farmers can minimize waste and reduce environmental impact while maximizing crop yields.
Another innovative technology that is gaining traction in Cambodia is vertical farming. This method involves growing crops in vertically stacked layers, often in controlled environments such as greenhouses or indoor facilities. Vertical farming allows for year-round production, regardless of weather conditions, and requires significantly less land and water compared to traditional farming methods.
Furthermore, the use of drones in agriculture has proven to be a game-changer in Cambodia. These unmanned aerial vehicles can be equipped with sensors and cameras to monitor crop health, detect pests and diseases, and even spray pesticides or fertilizers with precision. Drones enable farmers to quickly identify and address issues, leading to improved crop yields and reduced reliance on harmful chemicals.
Additionally, the adoption of smart irrigation systems has been instrumental in promoting sustainable agriculture in Cambodia. These systems utilize sensors and data analysis to determine the precise water requirements of crops, ensuring that they receive just the right amount of water at the right time. By minimizing water wastage, smart irrigation systems contribute to water conservation efforts and enhance overall agricultural productivity.
Last but not least, the integration of blockchain technology in the agricultural sector is gaining momentum in Cambodia. Blockchain provides a transparent and secure platform for recording and verifying transactions, enabling farmers to establish trust with buyers and access fair prices for their produce. This technology also facilitates traceability, allowing consumers to track the origin and quality of the food they consume.
- Precision farming techniques optimize resource utilization
- Vertical farming enables year-round production with minimal land and water requirements
- Drones revolutionize crop monitoring and pest control
- Smart irrigation systems minimize water wastage and enhance productivity
- Blockchain technology promotes transparency and fair trade in the agricultural sector
These innovative technologies hold great promise for sustainable agriculture in Cambodia, offering solutions to the challenges of limited resources, climate change, and food security. By embracing these advancements, Cambodia can pave the way for a more resilient and environmentally conscious agricultural sector.
Success Stories: Impact of Sustainable Farming on Ensuring Food Availability in Cambodia
In this section, we will explore the remarkable success stories that highlight the positive effects of implementing sustainable farming practices in Cambodia. Through the adoption of innovative techniques and the promotion of environmentally friendly approaches, sustainable agriculture has significantly contributed to enhancing food availability and reducing food insecurity in the country.
1. Empowering Smallholder Farmers
One of the key success stories of sustainable farming in Cambodia is the empowerment of smallholder farmers. By providing them with training, resources, and access to markets, sustainable agriculture initiatives have enabled these farmers to improve their productivity and income. This empowerment has not only enhanced their livelihoods but also contributed to the overall food security of the nation.
2. Diversification of Agricultural Practices

Sustainable agriculture has played a crucial role in diversifying agricultural practices in Cambodia. Farmers are now encouraged to adopt crop rotation, agroforestry, and integrated pest management techniques. This diversification has not only reduced the reliance on a single crop but also improved soil fertility, minimized pest outbreaks, and increased overall agricultural productivity. As a result, the availability of diverse and nutritious food options has increased, contributing to improved food security.
- Integrating livestock into farming systems
- Implementing organic farming methods
- Promoting the cultivation of indigenous crops
3. Strengthening Resilience to Climate Change
Sustainable farming practices have also played a vital role in enhancing the resilience of Cambodian agriculture to climate change. By promoting the use of climate-smart techniques such as conservation agriculture and water-efficient irrigation systems, farmers have been able to adapt to changing climatic conditions. This resilience has ensured a stable food supply even in the face of extreme weather events, ultimately improving food security for vulnerable communities.
These success stories highlight the transformative impact of sustainable farming practices on food security in Cambodia. By empowering smallholder farmers, diversifying agricultural practices, and strengthening resilience to climate change, sustainable agriculture has not only improved food availability but also contributed to the overall well-being of the nation.